You don't need a huge software vocabulary to work with DocuWare. Most terms used in the program are derived from when we mostly filed paper documents. This makes it super easy to get started. And if you need any help, you'll know exactly what to ask for.
With these 10 terms, you can easily explain to new employees what's important in DocuWare. (Missing something here? Let us know in the comment section!)
Archive
An archive or a file cabinet is a digital memory, where documents are stored along with their ↑index terms. To view a document, you search and retrieve documents from a file cabinet. Archiving is also commonly used to describe how documents are stored in a file cabinet.
Client
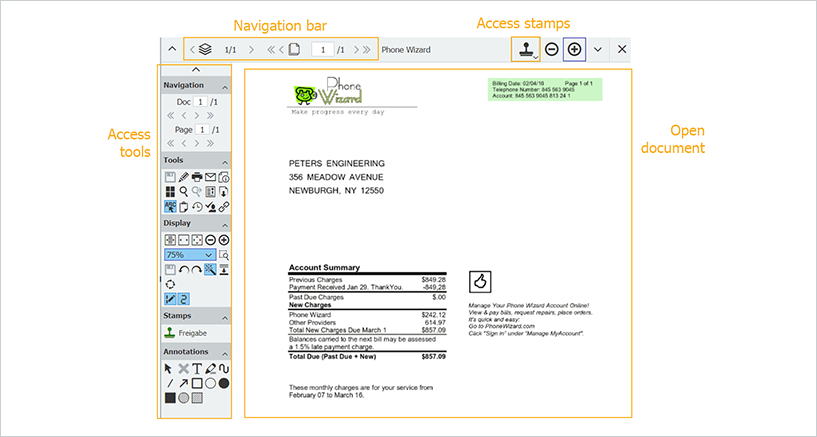
You work with ↑DocuWare in a browser like Edge, Chrome or Firefox. This is known as the DocuWare Client. This is where you view documents, see an overview of your tasks and ↑lists, and customize your personal profile:
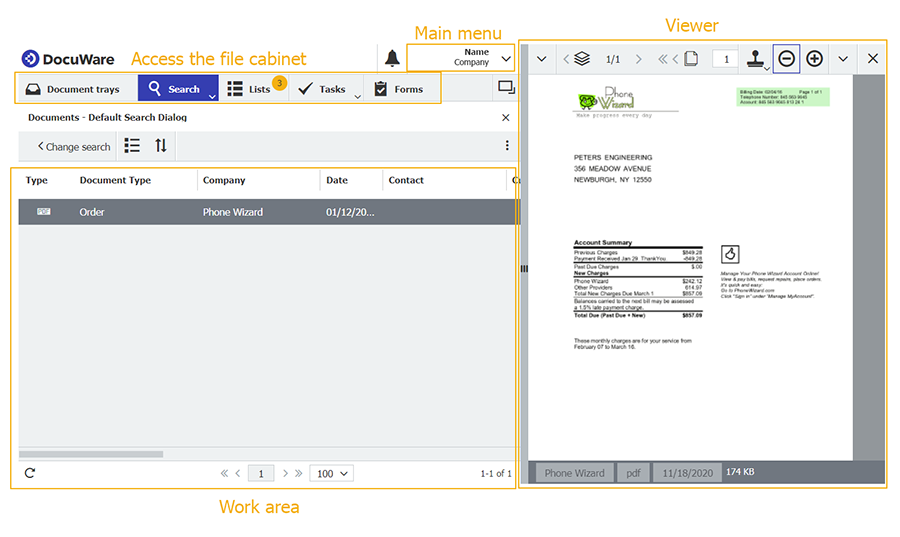
Configuration
Almost everything that happens in ↑DocuWare is based on some type of pre-set configuration. For example, automatic import. This determines which documents should be imported, stored in which file cabinet, how they are named and indexed. Even file cabinets, permissions or ↑lists are based on configurations. Which features may be configured by employees also depends on their ↑permissions:
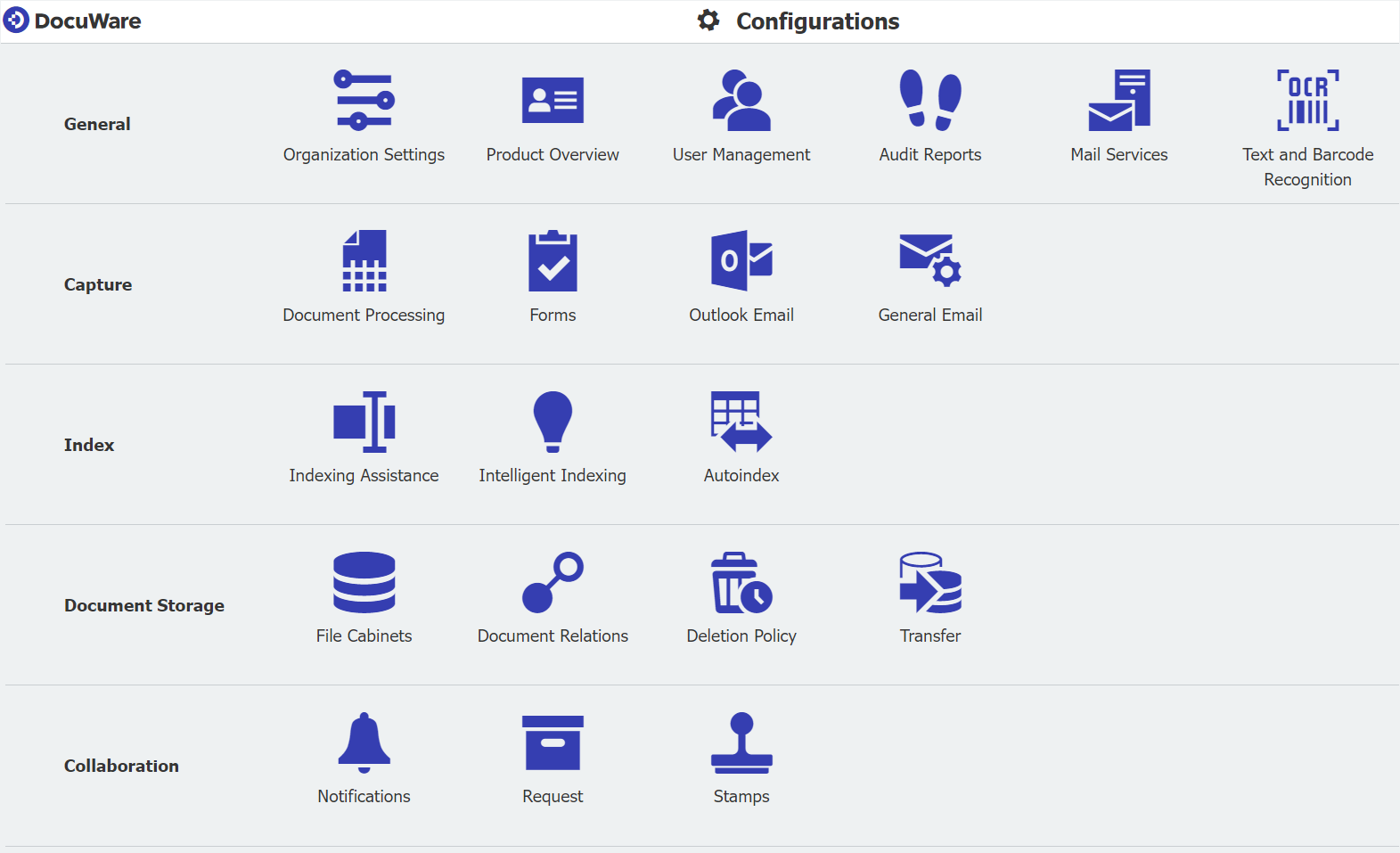
DocuWare
"DocuWare" is often used interchangeably with "↑archive". Saving in DocuWare means importing a document, ↑indexing it and storing it in a tamper-free, audit-proof manner. DocuWare may also run quasi invisibly within another application – for example, when email is automatically imported from Outlook.
Index
To find and retrieve a document conveniently from an ↑archive, it’s best to index a document when storing it with terms captured from a document‘s content along with the person filing it and the document type.
List
You can see lists in ↑DocuWare Client, alongside search/store dialogs and the ↑viewer. A list shows the documents that are waiting to be processed, which are highlighted in a special color.
Permissions
If an employee is unable to access a feature, the reason is often a lack of authorization. Documents, users and ↑configurations are protected with a complex system of permissions. If in doubt, ask your DocuWare Administrator.
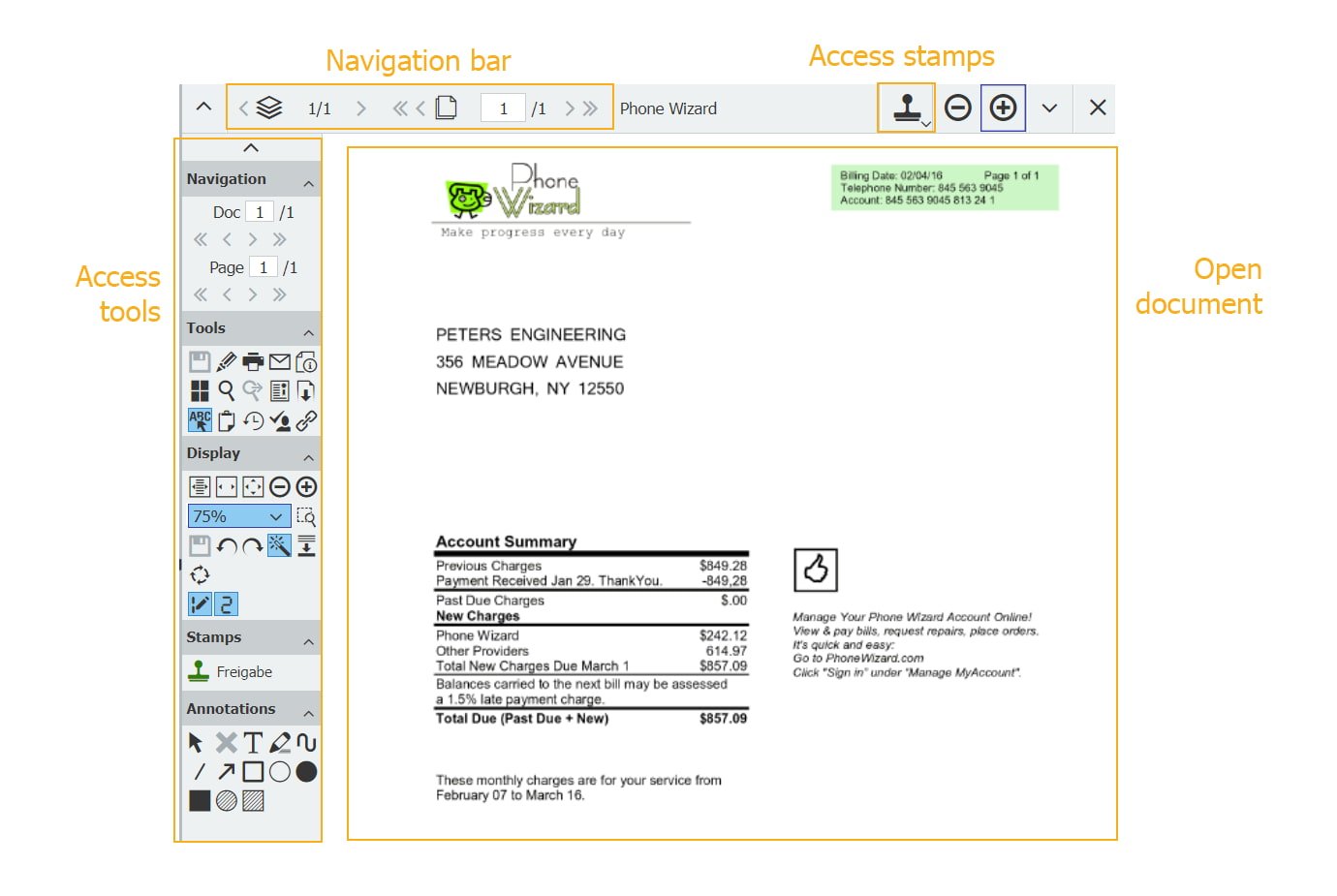
Stamp
Like its paper counterpart, you can also place a DocuWare stamp on a document - for example, to approve an invoice in your ↑list. Stamps are available in the ↑viewer.
Tray
A document tray is like the good old document in-box on your desk. Here, documents are collected before they are stored in a file cabinet (↑archive). In a tray, documents can be sorted, stapled, and edited - among other things.
Viewer
The viewer, used for displaying documents, is part of the ↑DocuWare Client. Besides stamps, many other tools are available in the viewer, such as one-click indexing, comments, zoom and much more.
Along with these DocuWare terms, you can also provide your new colleagues with these articles in the DocuWare Knowledge Center: Getting started with DocuWare.
Other readers also found this interesting:
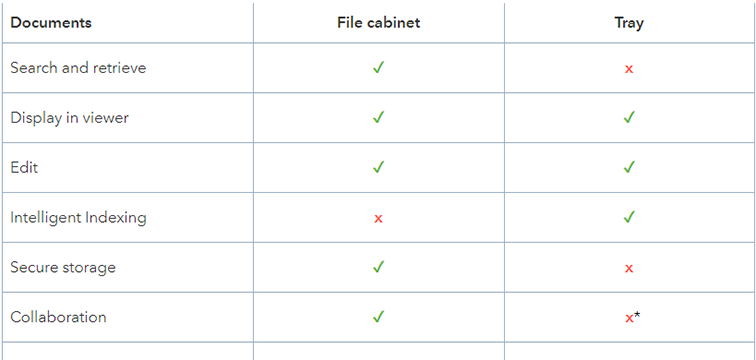 |
Not just for newbies: the advantages of trays and file cabinets |
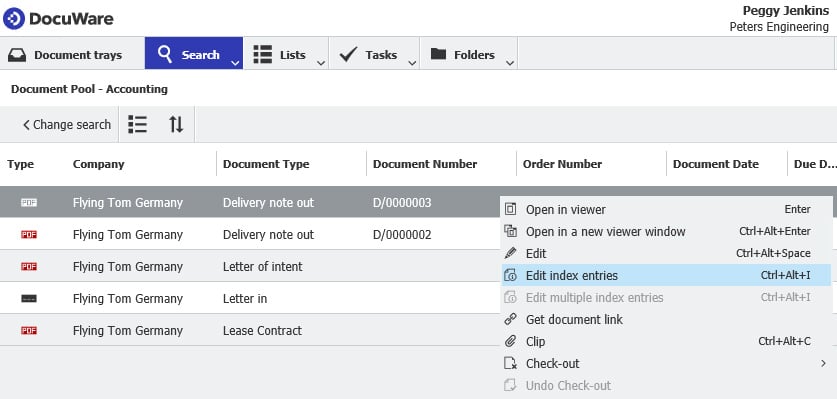 |
Index terms: a brief introduction Index terms can be a document‘s name, type of document, contact person, date or any other category. Learn more about they key role they play in DocuWare for identifying documents and triggering workflows.
|
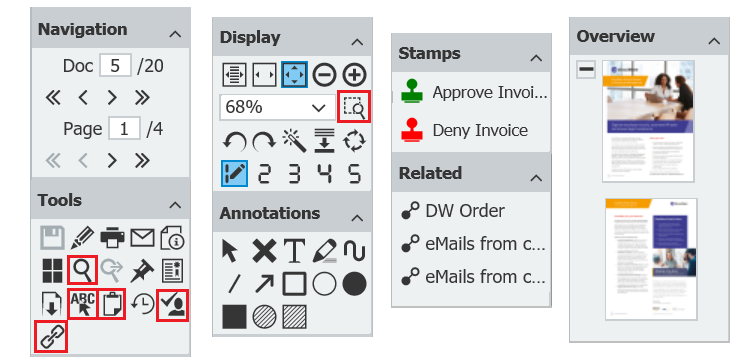 |
Grab the tool you need for your task The DocuWare Viewer can do so much more than just display documents. Over 60 functions can be launched via its toolbars. Here’s how you pick exactly the one you need for your actual task.
|